5 Common Types of Arthritis
We look at five common types of arthritis and break it down for you.
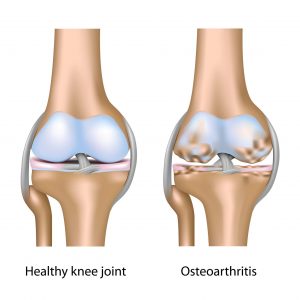
Osteoarthritis
This is the most common type of arthritis, especially among older people. Osteoarthritis is a joint disease that mostly affects the cartilage. Cartilage is the slippery tissue that covers the ends of bones in a joint. Healthy cartilage allows bones to glide over one another and absorbs energy from the shock of physical movement.
With osteoarthritis, the articular cartilage that covers the ends of bones in the joints gradually wears away. This allows bones under the cartilage to rub together, causing pain, swelling and loss of motion of the joint.
Symptoms
- Recurring pain in the affected joint(s) or muscles around the joint after a period of prolonged or strenuous use
- Stiffness
- Limited joint motion
- Tenderness and occasional swelling
- Joint deformity
- Joint cracking
There is currently no cure for osteoarthritis and the condition is irreversible. Stick to gentle exercises such as walking, biking or swimming. Exercise can increase your endurance and strengthen the muscles around your making, making your joint more stable. Maintain a healthy weight to relieve pressure and apply over-the-counter pain creams to provide temporary relief. Surgery is generally reserved for severe cases.
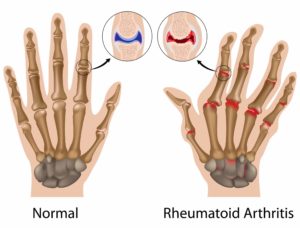
Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA)
This is a disease of the immune system that affects multiple joints in the body. It can lead to long-term joint damage, resulting in chronic pain, loss of function and disability. It attacks the lining of your joints, causing swelling that can result in aching, throbbing joints and eventually deformity.
Symptoms
- Swelling and painful joints
- Joints that are warm and tender to the touch
- Morning stiffness that lasts at least 30 minutes
- Red and puffy hands
- Firm bumps of tissue under the skin on your arms
- Fatigue
- Low grade fever
- Loss of appetite, weight loss
Risk factors for RA include family history of RA, smoking and hormonal changes during pregnancy or viruses. There is no cure for RA. Treatment for RA aims to reduce inflammation in your joints to relieve pain and prevent or slow joint damage through exercise and eating a healthy diet. Treatment typically involves medications and surgery, if necessary, in cases of severe joint damage.
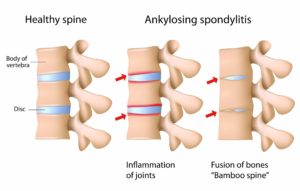
Ankylosing Spondylitis
This is a form of chronic inflammation of the spine and the sacroiliac joints and can affect other tissues throughout the body. Chronic inflammation causes pain and stiffness in and around the spine. Overtime, ankyloses leads to loss of mobility of the spine.
Symptoms
- Lower back pain
- Stiffness and limited motion in the low back
- Hip pain and stiffness
- Limited expansion of the chest
- Limited range of motion, especially involving spine and hips
- Joint pain and joint swelling in the shoulders, knees and ankles
- Neck and heel pain
- Chronic stooping to relieve symptoms
- Fatigue
- Fever
- Loss of appetite, weight loss
- Eye inflammation
Risk factors include family history. There is currently no cure for ankylosing spondylitis but the condition is not beyond help. Treatments centre on alleviating the symptoms and managing the progression of the condition to regain mobility of the spine through medicine and exercise.
Fibromyalgia
There is no inflammation of the affected muscles and no damage to the structure of the joints or soft tissues. Common sites of pain include the neck, back, shoulders, pelvic girdle and hands. Pain generally lasts for months. People with fibromyalgia have a lower threshold for pain because of increased sensitivity in the brain to pain signals.
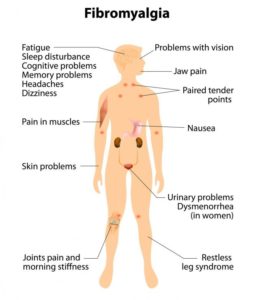
Symptoms
- Widespread musculoskeletal aches, pain and stiffness
- Sleep disturbances
- Headaches
- Impaired memory
- Dizziness
- Diarrhoea and/or constipation
- Anxiety or depression
Risk factors include family history, psychological stress, hormonal changes and injury. Decreased blood flow to muscles may contribute to decreased strength and fatigue and may play a role as well.
Fibromyalgia has no cure. A proper and regular sleep can improve sleep and provide relief.
Gout
Gout is caused by an overproduction of uric acid or a reduced ability of the kidney to get rid of uric acid. It appears as an acute attack often coming on overnight. The joints commonly affected by gout are the big toe, foot, ankle, heel, instep and knee.
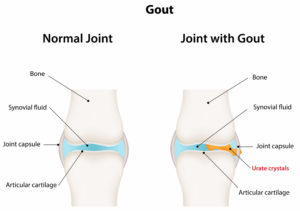
Symptoms
- Sudden, warm throbbing of affected joint(s)
- Pain and swelling
- Extreme tenderness in a joint (usually a big toe joint)
Risk factors for this condition includes obesity, family history, high alcohol intake and contribution from other diseases.
There is currently no cure for gout, but the symptoms can be controlled by medication and special diet. Restrict or avoid foods like liver, kidneys, red meat, shellfish, scallops, peas, lentils and beans.
